Multi-antenna UWB anchor nodes will play a crucial role in next-generation UWB applications to reduce infrastructure cost by leveraging joint distance and angle-of-arrival estimation techniques, to improve wireless data rates by exploiting (massive) MIMO techniques, and to include sensing functionality.
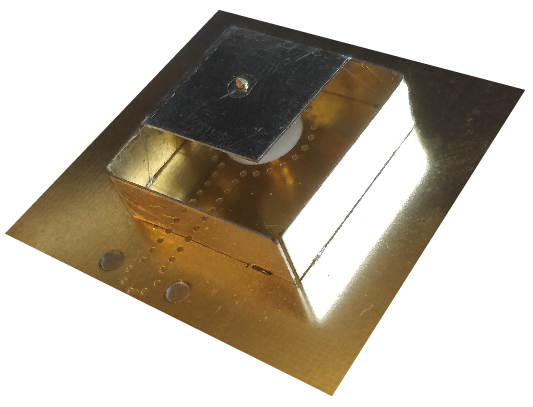 |
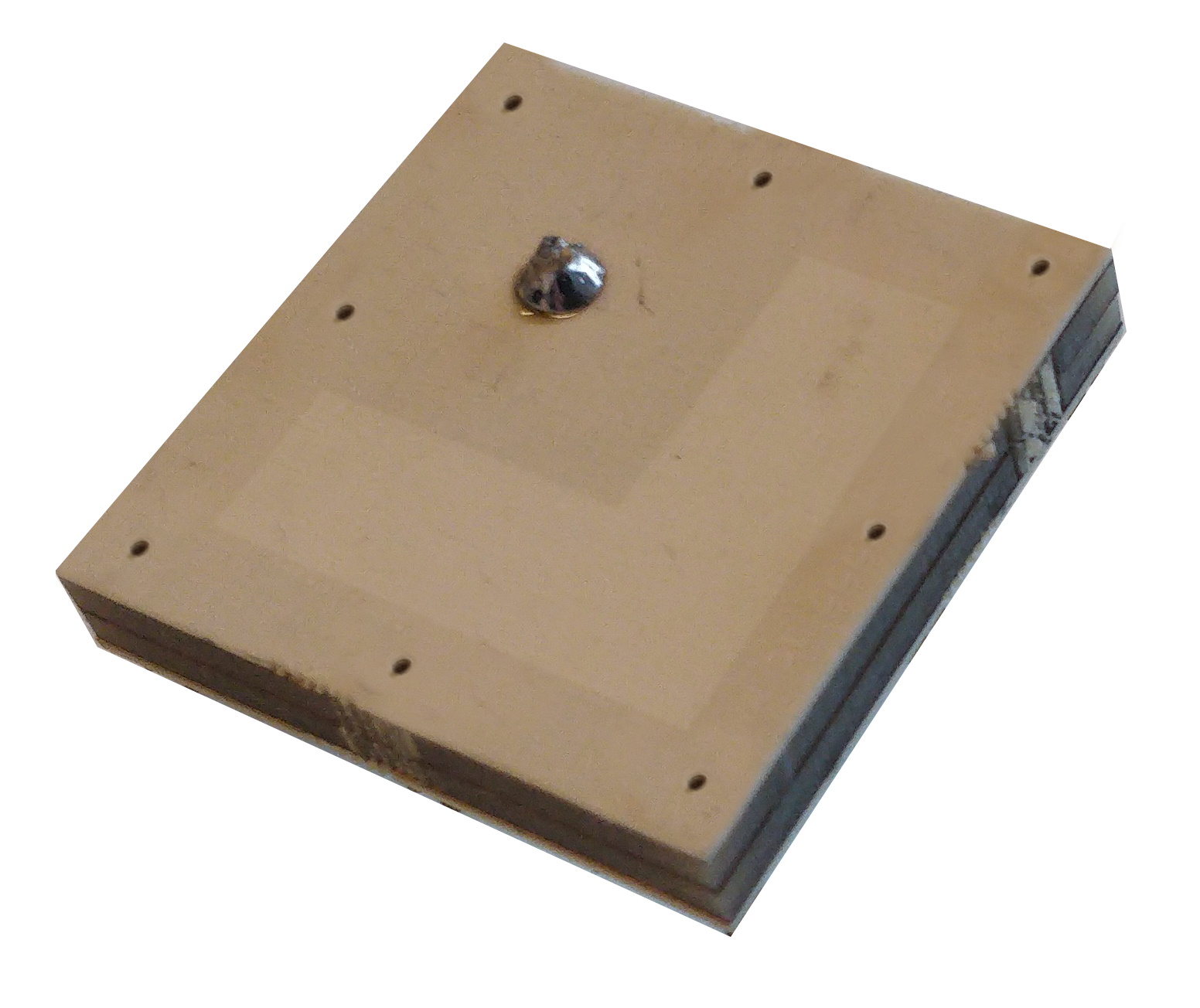
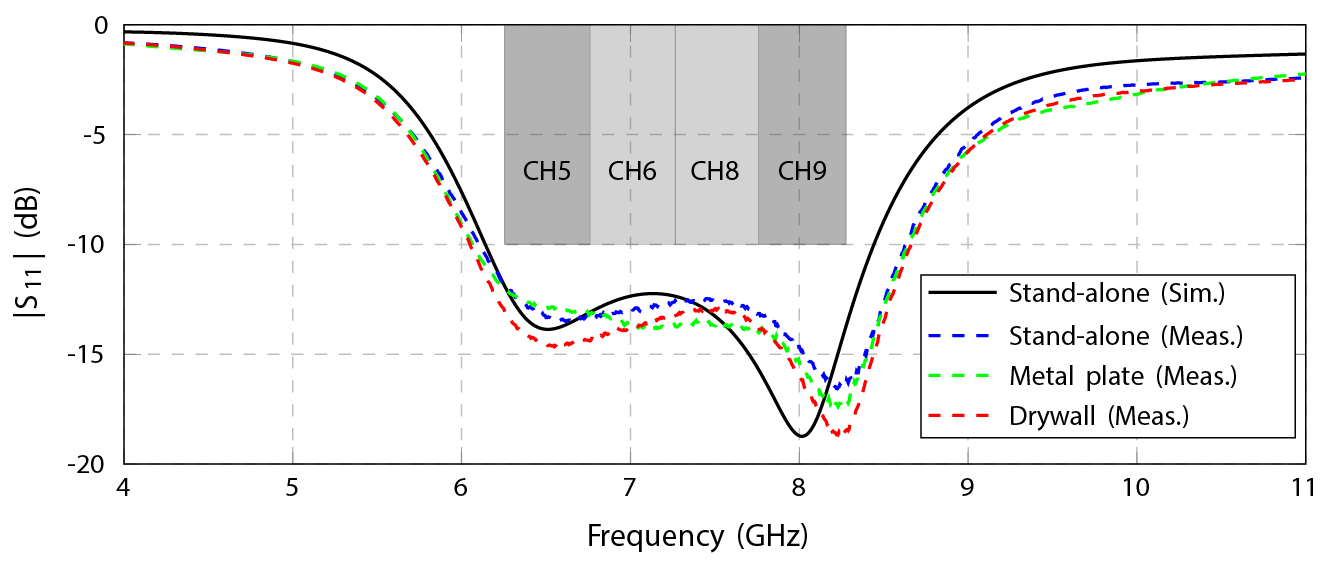
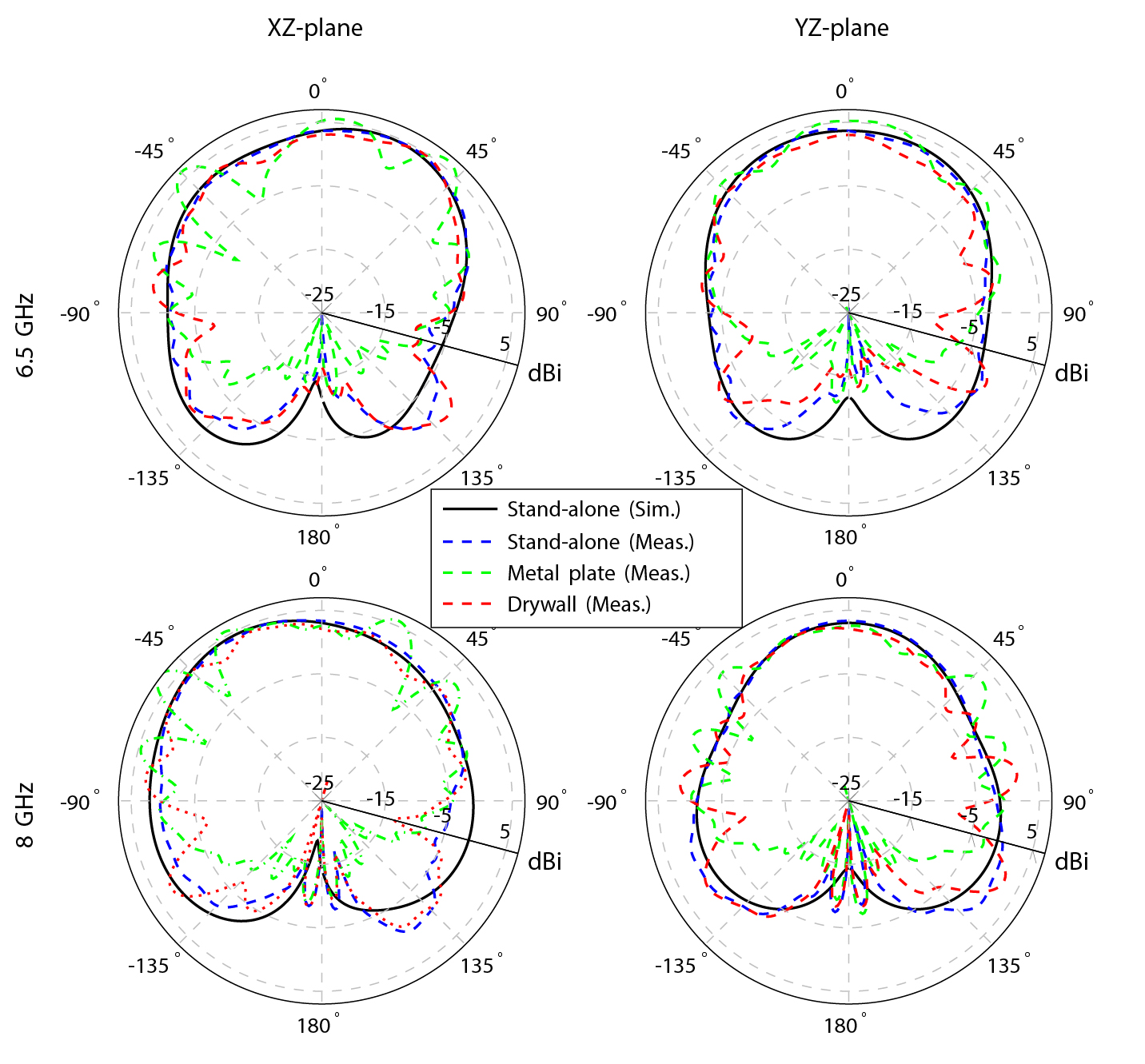
To address this need, our patented UWB antenna technology is leveraged to conceive an innovative UWB antenna element that provides best-in-class performance in the most compact footprint and enables multi-channel support. It covers channels 5 to 9 of the IEEE 802.15.4z standard, fits in a footprint of only 17.5 mm x 17.5 mm x 3.4 mm [0.43λ] (electrical size), and does not require a clearance area. Moreover, it features a minimum radiation efficiency of 90 %, a stable broadside gain of at least 4.9 dBi, and excellent time domain performance (system fidelity factor > 99 % and group delay variation < 68 ps). By confining the antenna fields to miniaturized air-filled regions and only allowing radiation through a judiciously engineered slot, they not only feature near-100 % radiation efficiency, but also provide a very high antenna-to-integration-platform isolation which makes them extremely robust and easy to integrate. |
Reflection coefficients
 |
Radiation patterns
 |
| By adopting partial-mode miniaturization techniques and leveraging an innovative antenna feed, Air-Filled-based UWB antennas not only offer a broadband 50 Ω interface, but can also be tailormade, facilitating co-design/optimization of the UWB antenna with the UWB transceiver and/or other front-end modules. This approach does not only maximize coverage, but also enables compact IC integration, leading to the smallest possible system footprint. |
 |
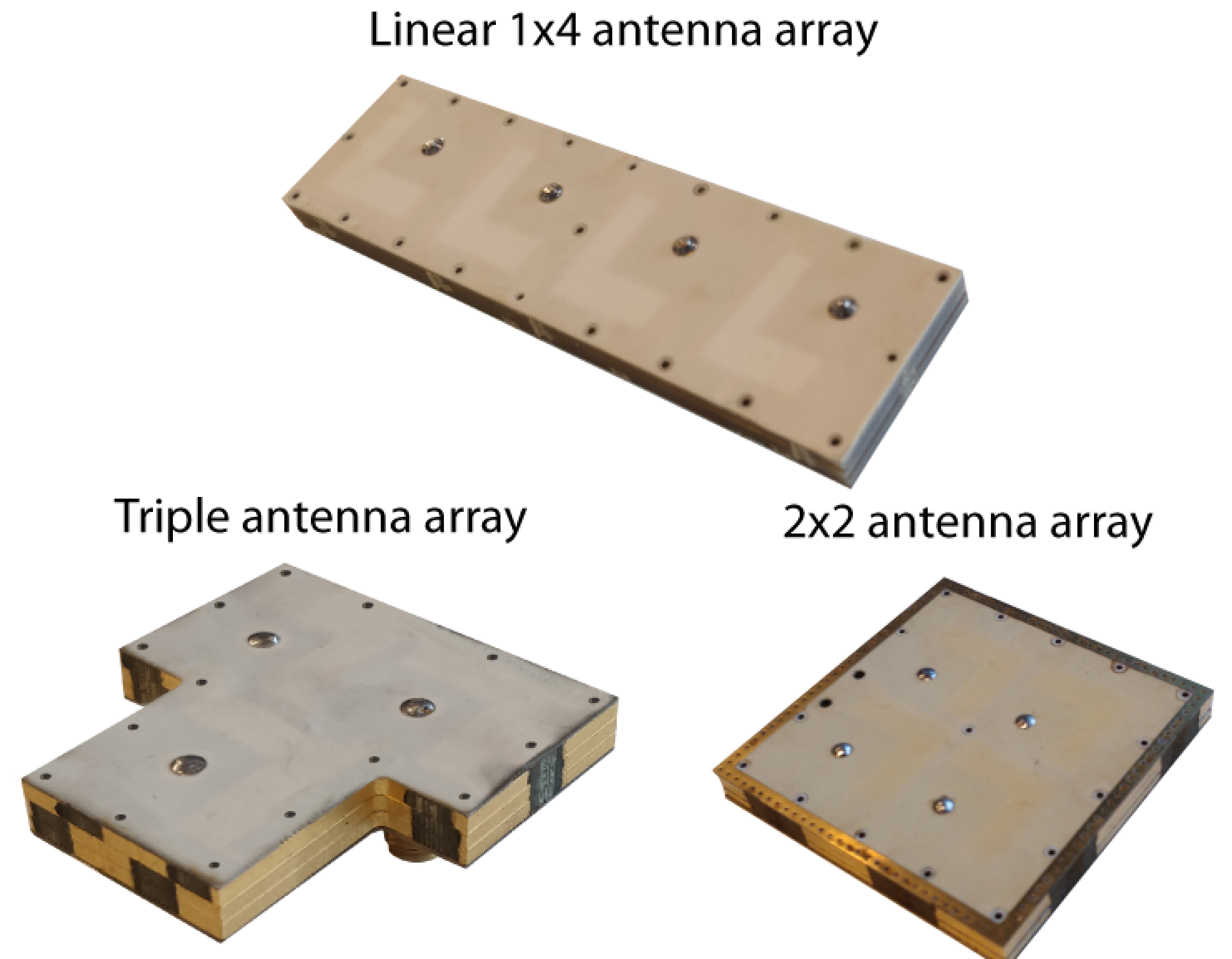 |
Owing to the inherent self-shielding of the Air-Filled-based UWB antennas, they serve as ideal building blocks for scalable planar multi-antenna IR-UWB systems that enable joint distance and 2D angle-of-arrival (AoA) estimation, improve TX-to-RX isolation and provide excellent MIMO performance, while significantly simplifying array calibration by providing stable performance in harsh real-life environments. |





